卷积在 CNN 中是非常基础的一个操作, 但是, 一旦写出来, 要画不少的图, 所以, 一直拖了下来, 刚好最近看到一个比较好的图, 能够说明卷积转化为矩阵相乘就行操作的方法.
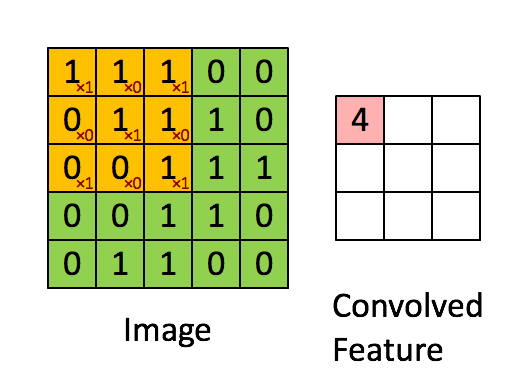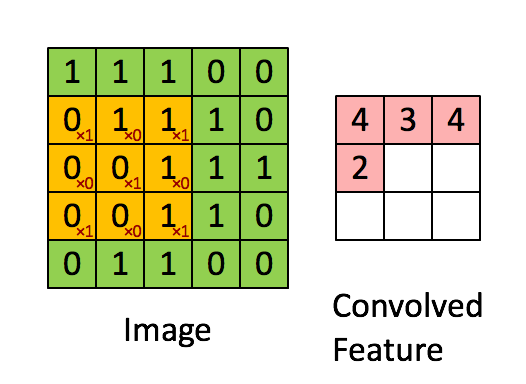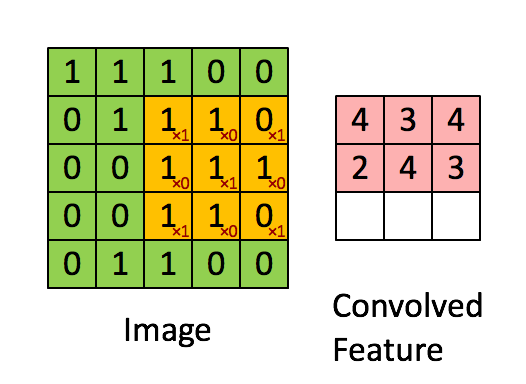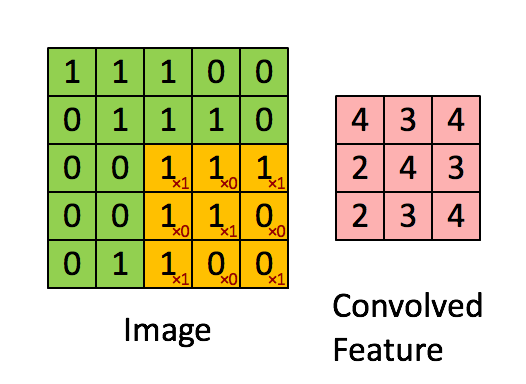
上图展示的是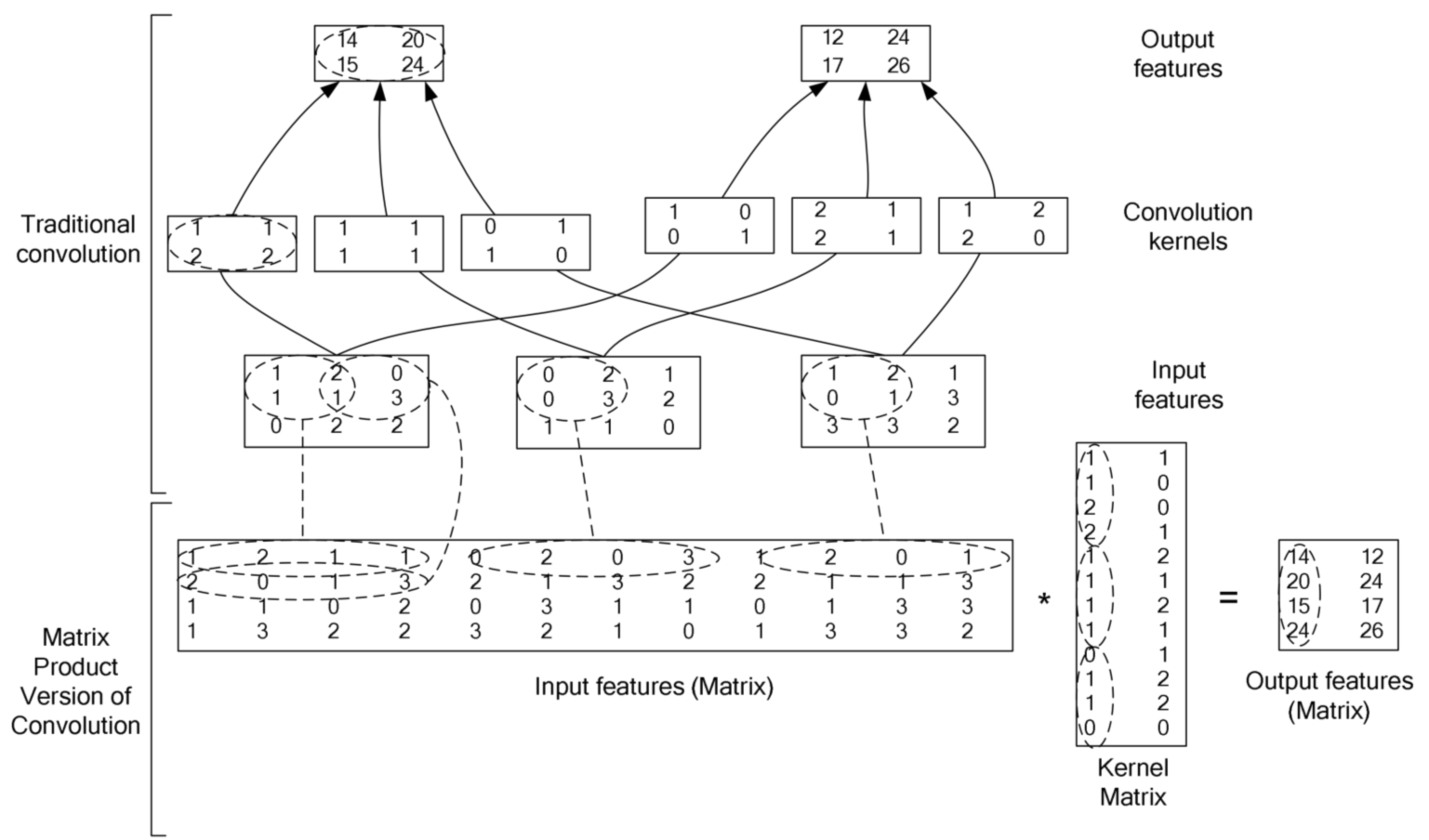
卷积操作的定义
卷积就是卷积核和另外一个矩阵 (图片) 对应位置相乘然后结果相加.

上图展示的是
stride=1 的情形, 既每次移动一个像素的位置, 根据需求, 也可以使用其他的 stride
卷积计算的加速
对于大的卷积核, 加速方法一般是使用傅里叶变换 (或者其加强版: 快速傅里叶变换), 但是, 对于比较小的卷积核, 其转换到频域的计算量已经大于直接在空域进行卷积的计算量, 所以, 我们会发现在主流的深度学习框架中, 一般是直接在空域中进行卷积计算, 其加速计算的方法就是把卷积操作转换成矩阵相乘 (因为有很多优化了的线性代数计算库和 CUDA), 下面这张图充分说明了具体过程 (2 维的情形).

- 在上图中,
input features每一个二维矩阵对应与 RGB 图像的 channel 或者是 feature map 中的 channel - 目前常见的卷积都是 cross channel 的卷积, 既卷积核矩阵是 3 维的 (width, height, depth), depth 的大小和 feature map 的 depth.(depth 就是有几张 feature map, 不要被高大上的名词迷惑了)
- 维卷积核的方法与 2 维的类似, 也是与 feature map 中相应的一个 3 维的矩阵对应位置元素相乘然后相加
- 2 维的卷积相当于 depth=1 的 3 维的卷积