Node.js底层有三个重要部分
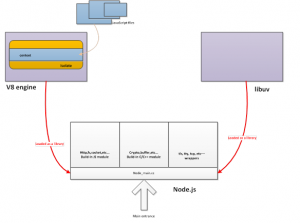
libuv 建立事件循环
v8 引擎以及JS/C++对象转换
node提供的模块 fs os net process等
libuv是一个神器,事件循环,适合状态机驱动的架构,单独学习。
v8的请看google的官方API文档。
今天主要看一下node的模块。
1.js2c.py
node内置了很多js文件,包括主程序 src/node.js和模块文件lib/*.js。js2py是把每一个js文件都生成一个源码数组,存放在node_natives.h中。
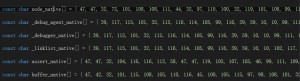
node_native.h中,每个js文件对应一个数组,源码以const char数组的形式存放。
node_native在映射完毕后,变成了这样一个数组。
2.node_javascript.cc
node_javascript.cc include了node_native.h,并提供两个方法:
MainSource(),只有一句
return OneByteString(env->isolate(), node_native, sizeof(node_native) - 1);
返回node_native映射的js文件,即node.js,转换成了一个v8::handle类型。
图:node_native,node.js映射后的数组。
DefineJavaScript(env, target)
将所有js文件映射到Object型的target(不包括node.js)
target->Set(name, source)
综上,node_javascript.cc做了两件事,返回node.js的v8::handle,
返回lib/*.js的Object,{name: v8::handle, name: v8::handle .....}
现在所有js文件都被转换成了v8::handle。
3.node.cc
node.cc是nodejs的main文件,这里我们先认识一个node世界中的风云人物,process。
在node.cc的CreateEnvironment函数中,process出生了,下面我们从源码看看process是个什么?被赋予了哪些属性?
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
Local<FunctionTemplate> process_template = FunctionTemplate::New(isolate); process_template->SetClassName(FIXED_ONE_BYTE_STRING(isolate, "process")); Local<Object> process_object = process_template->GetFunction()->NewInstance(); env->set_process_object(process_object); SetupProcessObject(env, argc, argv, exec_argc, exec_argv); |
从上面这段代码可以看出process的原始属性,FunctionTemplate,很明显,是js里的一个function,function的name为process。
现在JS世界中已经多了一个叫process的function,那么它是在哪里成长的呢?
在node.cc的LoadEnvironment函数中,
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
Local<String> script_name = FIXED_ONE_BYTE_STRING(env->isolate(), "node.js"); Local<Value> f_value = ExecuteString(env, MainSource(env), script_name); CHECK(f_value->IsFunction()); Local<Function> f = Local<Function>::Cast(f_value); Local<Object> global = env->context()->Global(); Local<Value> arg = env->process_object(); f->Call(global, 1, &arg); |
运行MainSource
拿到了node.js的返回f_value,即node.js函数,入参为process的闭包函数,
(function(process) {})
验明正身,执行node.js闭包函数,最后一句做JS的同学看着肯定很眼熟,这不就是
(function(process){}).call(global, process)
4.fs.js
这里通过一个fs模块的创建与加载,来展示process呼风唤雨的能力。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
const SlowBuffer = require('buffer').SlowBuffer; const util = require('util'); const pathModule = require('path'); const binding = process.binding('fs'); const constants = require('constants'); const fs = exports; const Buffer = require('buffer').Buffer; const Stream = require('stream').Stream; const EventEmitter = require('events'); const FSReqWrap = binding.FSReqWrap; const FSEvent = process.binding('fs_event_wrap').FSEvent; |
首先规规矩矩的加载了几个模块,然后突然出现了binding
Binding在node.cc中实现
主要逻辑为,查看cache中是否有这个模块,如果没有就新建一个。
新建模块:如果存在builtin,则使用nm_context_register_func方法注册到cache中,如果是常量,cache中注册常量,如果是natives,绑定所有lib/*.js。
在fs中,process.binding找到了fs,是一个builtin模块。这个模块在node_file.cc中实现,最后通过NODE_MODULE_CONTEXT_AWARE_BUILTIN注册到builtin。
Binding函数完成了js上调用C++模块。
5.node.js
node.js中通过一个NativeModules来管理js模块,
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
function NativeModule(id) { this.filename = id + '.js'; this.id = id; this.exports = {}; this.loaded = false; } NativeModule._source = process.binding('natives'); NativeModule._cache = {}; |
process.binding('natives'),将所有内置js模块绑定到_source上。
之后可以通过require方法来拿到这些模块。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
NativeModule.require = function(id) { if (id == 'native_module') { return NativeModule; } var cached = NativeModule.getCached(id); if (cached) { return cached.exports; } if (!NativeModule.exists(id)) { throw new Error('No such native module ' + id); } process.moduleLoadList.push('NativeModule ' + id); var nativeModule = new NativeModule(id); nativeModule.cache(); nativeModule.compile(); return nativeModule.exports; }; |
先检查cache,如果cache没有,就在process.moduleLoadList中增加一个,然后缓存,执行.
缓存就是把模块放到_cache中,compile函数
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
NativeModule.prototype.compile = function() { var source = NativeModule.getSource(this.id); source = NativeModule.wrap(source); var fn = runInThisContext(source, { filename: this.filename, lineOffset: 0 }); fn(this.exports, NativeModule.require, this, this.filename); this.loaded = true; }; var ContextifyScript = process.binding('contextify').ContextifyScript; function runInThisContext(code, options) { var script = new ContextifyScript(code, options); return script.runInThisContext(); } |
通过C++模块contextify运行了这段js。