假设spring配置文件为applicationContext.xml
一.Spring配置文件在类路径下面
在Spring的Java应用程序中,一般我们的Spring的配置文件都是放在放在类路径下面(也即编译后会进入到classes目录下)。
以下是我的项目,因为是用maven管理的,所以配置文件都放在"src/main/resources"目录下,这时候,在代码中可以通过
|
1 |
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); |
然后获取相应的bean。
如果代码想用Junit测试框架来测试,则Spring提供了对Junit支持,还可以使用注解的方式:
|
1 2 |
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration(locations={"classpath:applicationContext.xml"}) |
只需要在相应的Test类前面加上此两个注解(第二个注解用来指明Spring的配置文件位置),就可以在Junit Test类使用中Spring提供的依赖注入功能。
二.Spring配置文件在WEB-INF下面
当然在做J2EE开发时,有些人习惯把Spring文件放在WEB-INF目录(虽然更多人习惯放在类路径下面)下面,或者有些Spring配置文件是放在类路径下面,而有些又放在WEB-INF目录下面,如下图:
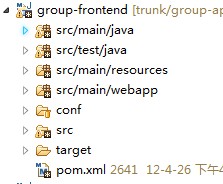
这时候,在代码中就不可以使用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext来加载配置文件了,而应使用FileSystemXmlApplicationContext。
|
1 |
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml"); |
然后获取相应的bean。
如果代码想用Junit测试框架来测试,则Spring提供了对Junit支持,还可以使用注解的方式:
|
1 2 |
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration(locations={"file:src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml"}) |
只需要在相应的Test类前面加上此两个注解(第二个注解用来指明Spring的配置文件位置),就可以在Junit Test类使用中Spring提供的依赖注入功能。
下面是我的一个Spring管理下的Junit测试类:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
import java.util.List; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration({"file:src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml"}) public class SuFriendServiceImplOverRMITest { @Autowired private SuFriendService suFriendService; @Test public void getUserFollowerListTest(){ List list = suFriendService.getUserFollowerList("liug_talk@163.com"); System.out.println("------"+list); } } |